It’s a fine, translucent ceramic made from kaolinite clay, fired at high temperatures to achieve its strength and delicate, glass-like quality. Used in art, tableware, and technology, it’s renowned for its purity and durability.
Introduction
It’s the aristocrat of ceramics, really. Born from the purest kaolinite clay and transformed in the fiery belly of a kiln, porcelain emerges as the strongest, most translucent member of the ceramic family. Now, if you’re itching for a deep dive into its storied past and how it stands tall among its earthenware and stoneware cousins, take a gander at my musings on Artabys. Here, I’ve laid out the entire saga from its humble beginnings to its global triumph.
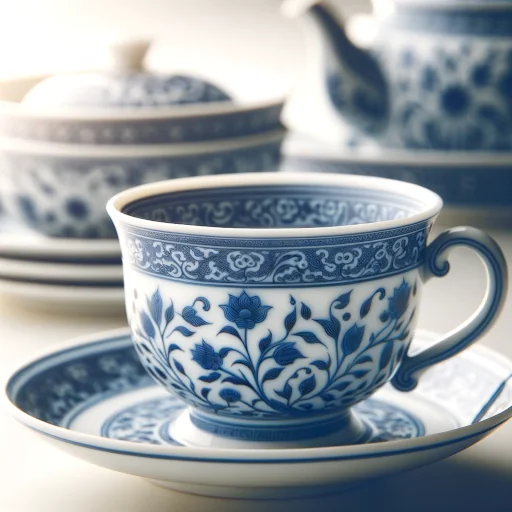

Porcelain’s Pedigree
- The Elite of Ceramics: Unlike its kin, porcelain is known for its finesse and resilience.
- Translucency and Purity: It has a certain je ne sais quoi, with a glassy sheen that’s second to none.
- Cultural Heirloom: Porcelain’s not just a material; it’s a piece of history, carrying tales from ancient dynasties to your very dinner table.
For a crisp comparison that sets porcelain apart from the ceramic pack, have a peek at my piece on the difference between ceramic, pottery, and porcelain. Trust me, it’s quite the enlightening read!
The Science Behind Porcelain
Let me take you on a little scientific journey behind the magic of porcelain. It’s not just an art; it’s a symphony of chemical and physical transformations that begin with the right choice of earth and end with a masterpiece that could last for ages.
The Alchemy of Firing
- Transformation Under Fire: When kaolinite-rich clay hits temperatures north of 1200°C, it undergoes a metamorphosis, bidding adieu to its humble beginnings.
- Vitrification Station: At these scorching heights, the clay starts to vitrify, turning partially glassy, which is what gives porcelain its trademark translucence and strength.
- Mullite Creation: This is where mullite comes into play, a mineral that forms in the heat and acts like the backbone of porcelain, ensuring it doesn’t crumble under pressure.
The Evolution of Excellence
- Kiln Innovations: Gone are the days of hit-or-miss firing. Modern kilns offer precise temperature control, making sure every piece comes out just as intended.
- Glaze Chemistry: We’ve become alchemists, concocting glazes that don’t just dazzle but protect, thanks to understanding their molecular makeup.
- Digital Sculpting: 3D printing is the new kid on the block, allowing us to create porcelain pieces that were once deemed impossible.
It’s this fascinating interplay of art and science that keeps porcelain at the pinnacle of ceramic sophistication. And believe me, there’s always more to learn, more to improve. That’s what keeps an old timer like me forever young at heart.
The Art of Porcelain: Beyond Utility
Let’s talk about porcelain, not just as your grandmama’s tea set, but as a canvas for modern artists. It’s not all function these days; it’s a full-blown renaissance of form.
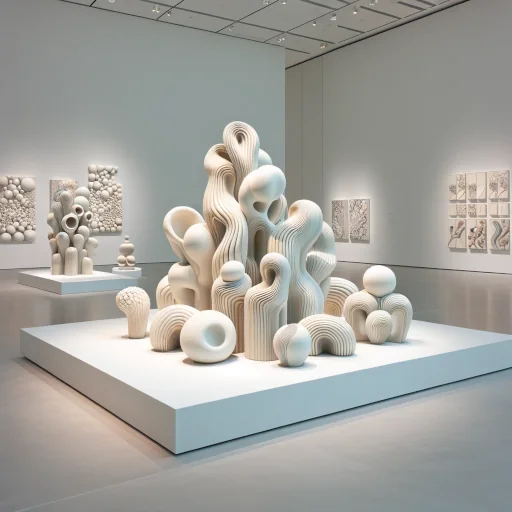

Porcelain Reimagined
- Sculptural Wonders: Artists are pushing boundaries, turning porcelain into avant-garde sculptures that challenge gravity and expectation.
- Painted Perfection: Forget simple glazes; we’re talking intricate hand-painted designs that tell stories, intricate enough to rival the old masters.
- Mixed Media Mashups: Porcelain’s mingling with unexpected partners, metals, resins, even digital elements, creating a new vocabulary in art.
Innovation on Display
- 3D Porcelain Printing: It’s the wild west of design right now, with artists printing, layer by minuscule layer, crafting pieces that were once just a pipe dream.
- Interactive Installations: Imagine walking through a forest of translucent leaves or witnessing a mural where figures seem to breathe.
This ain’t your run-of-the-mill craft. It’s a bold statement, a whispering shout in the halls of contemporary art. And as your trusty guide, I’m here to tell you: the world of porcelain art is just heating up, and it’s more exhilarating than ever!
Porcelain in Architecture and Design
Welcome to the grand tour of porcelain in the modern world, where it’s not just about dainty dishes anymore. Porcelain has stepped out of the china cabinet and onto the scene of architecture and interior design with a flair that’s both timeless and cutting-edge.
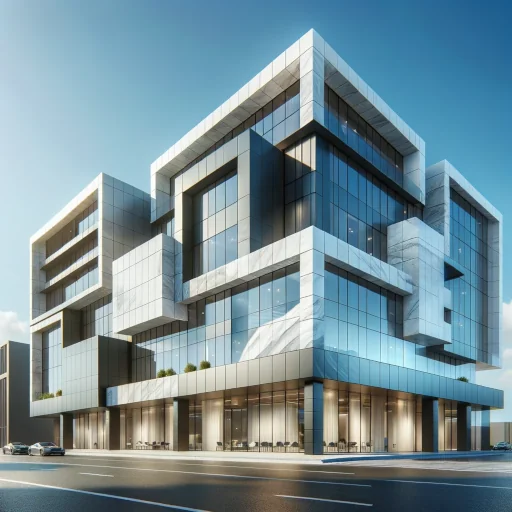

Porcelain’s New Frontier
- Facade Fashion: Buildings are donning porcelain as their exterior garb, boasting not just beauty but brawn, standing up to the elements with grace.
- Tile Transformation: Forget what you know about tiles. Porcelain is bringing drama to floors and walls with larger-than-life slabs and textures that can mimic everything from wood to marble.
- Furniture Fusion: Yes, you heard it right. Porcelain is sneaking into furniture, lending its sleek durability to tables, countertops, and even lighting fixtures.
Facade Fashion
In Münster, Germany, the H7 office building, a timber hybrid structure designed by Andreas Heupel Architects, showcases a stunning porcelain facade. The building is clad in ALPHATON® panels in varying shades of green, which change color with the light due to their semi-transparent glaze, giving the facade a lively, natural appearance.1
Tile Transformation
The Pantheon Iconic Hotel in Rome, with interior designs by Studio Marco Piva, utilizes porcelain stoneware not just as a surface coating but as a defining element of design. The hotel’s floors feature black lacquered marble-textured porcelain stoneware, echoing the grandeur of the ancient Pantheon and fusing modern minimalism with classical magnificence.2
Furniture Fusion
Porcelain stoneware has also made its way into furniture. It can be used to cover large surfaces such as tables or countertops with a single, thin slab. Moreover, these slabs can serve as decorative elements, adorning bed headboards, fireplace frames, or even doors and shutters, with custom designs available through advanced digital decoration techniques.
A Showcase of Elegance
- Visual Feast: Picture this – a lobby with walls cascading with porcelain art, reflecting the light, setting the place aglow.
- Design Dexterity: From urban chic to rustic charm, porcelain adapts, bringing designers’ most daring visions to life.
- Innovative Interiors: Imagine a bathroom with a seamless porcelain skin, sleek, hygienic, and utterly stunning.
Now, if you’re hankering for some real-life peeks into these wonders, a gallery of images would do the trick. You’d see porcelain’s versatility shine in skyscrapers and suburban homes alike, each piece a testament to this material’s remarkable journey from kiln to skyline.
Porcelain Around the World: A Global Perspective
From its birthplace in China, this prestigious material has been embraced and re-envisioned by cultures near and far. Each has infused it with a local flavor, crafting a story in clay that’s as diverse as it is beautiful.
The Eastern Mastery
- Japan’s Artisanal Pride: In Japan, porcelain is synonymous with regions like Arita. Here, artisans have perfected a blend of functionality and art, creating pieces that are deeply rooted in tradition yet strikingly modern.3
- Korea’s Celadon Elegance: Over in Korea, the focus has been on celadon, a type of porcelain known for its jade green glaze. It’s a craft that marries the country’s rich history with a penchant for understated beauty.
The Western Interpretation
- Germany’s Technical Precision: Jumping to Germany, the name Meissen strikes a chord. As Europe’s first porcelain manufacturer, German porcelain is a testament to technical prowess and artistic ambition, often depicting intricate, hand-painted scenes.4
- France’s Royal Affection: Not to be outdone, France’s Limoges has held the favor of royalty and nobility for centuries. The French have a knack for the ornate, favoring elaborate designs and a certain je ne sais quoi that speaks of luxury.5
The Cultural Exchange
- Adoption and Adaptation: Each culture’s take on porcelain tells a unique part of the material’s story. The exchange of ideas and techniques through trade routes has led to a beautiful amalgamation of styles.
- The Modern Canvas: Today, global influences converge, and contemporary creators draw inspiration across borders, making porcelain a true citizen of the world.
In the hands of different cultures, porcelain becomes a mirror reflecting their values, aesthetics, and history. It’s a fascinating journey that shows no sign of slowing down, with each chapter richer than the last.
The Future of Porcelain: Technology and Sustainability
As we stand on the cusp of a new era for porcelain, it’s clear that technology and a commitment to sustainability are steering the ship. This isn’t your ancestors’ porcelain; it’s smarter, cleaner, and ready to meet the future head-on.
The Tech Revolution
- 3D Printing: The world of porcelain has been revolutionized by 3D printing, allowing for the creation of shapes and designs that were once impossible. This technology minimizes waste as it uses only the necessary amount of material.
- Digital Design: Porcelain’s patterns are going digital, too. High-definition digital printing on porcelain surfaces is now possible, offering unlimited aesthetic options with reduced environmental impact.
- Advanced Kilns: Kilns have gone high-tech, with better insulation and energy efficiency. They can now fire porcelain at precisely controlled temperatures, which improves quality and reduces energy consumption.
3D Printing in Porcelain
One example of 3D printing in porcelain manufacturing comes from the College of Design at NC State University. Here, Shawn Protz, an assistant professor, integrates technology with traditional North Carolina pottery techniques. This innovative approach uses a 3D printer to process local clay, creating objects that combine the state’s rich pottery legacy with modern digital fabrication.6
Protz developed a script for the 3D printer that allows for the creation of custom ceramic objects, which could include complex textures and forms that are challenging to achieve by hand. The experimentation with this technology in the classroom has led to the production of vases, bowls, and even architectural elements like a screen wall installed on campus. This method not only enables the creation of intricate designs but also ensures precision and minimizes material waste.
These advancements in 3D printing technology are reshaping the future of porcelain, allowing for greater creativity and efficiency in its production. The potential for reducing waste is significant since 3D printing uses only the material that is needed for the object, avoiding the excess that can occur in traditional manufacturing processes. This is just one example of how technology is contributing to the evolution of porcelain artistry and manufacturing.
Advanced Kiln Technologies
- Keith Company’s Advanced Kilns: This company offers a range of advanced kilns, including box kilns, envelope kilns, shuttle kilns, and tunnel kilns, all designed for ceramic and porcelain firing. These kilns are engineered for precise temperature control and energy efficiency, allowing for consistent firing conditions that improve the quality of the final porcelain product while reducing energy consumption.7
Historical Context and Modern Improvements
- Evolution from Early Kilns: Traditional ceramics and porcelain have been sintered in kilns since the early Chinese designs, which reached temperatures above 1000°C. European advancements in kiln technology during the 18th century included improved refractories for higher temperatures and better heat distribution. The introduction of coal as a fuel source marked a significant step in achieving the high temperatures required for porcelain sintering.
- Shift from Sagger to Modern Kilns: Historically, quality bisque and glazed wares were often fired in saggers to protect them from direct flames and gases. However, the use of saggers has declined due to cleaner and more efficient firing methods with gas, oil, and electric kilns. Advances in raw materials preparation and forming have led to a reduction in reliance on saggers, with many large potteries now using more efficient muffle-type tunnel kilns, which are a type of advanced kiln.
These examples highlight how advanced kilns have made the porcelain manufacturing process more efficient and environmentally friendly. Modern kilns allow for fine-tuning the firing process, leading to a higher quality end product with less waste and reduced energy use. The evolution from traditional firing methods to the use of advanced kilns represents a significant technological advancement in the porcelain industry.
Embracing Sustainability
- Recycling Overdrive: Porcelain manufacturing now often includes recycling its own waste. The discarded material from production is ground down and reincorporated, reducing the need for raw materials.
- Eco-Friendly Glazes: The development of lead-free and non-toxic glazes is a game-changer. These new glazes are safer for both the environment and the artisans who work with them.
- Water Conservation: Modern porcelain facilities are adopting water recycling systems, significantly reducing the volume of water needed for the production process.
As we look to the future, it’s this blend of innovation and respect for the planet that promises to keep porcelain relevant and revered. It’s an exciting time to be part of the porcelain world, and I, for one, can’t wait to see where this blend of art, science, and consciousness takes us next.
Porcelain Care and Repair
As an expert in the field, I can tell you that porcelain is both resilient and delicate. Here’s how you can keep your porcelain in tip-top shape and what to do if an accident leaves you with a chip or a crack.
Caring for Your Porcelain
- Gentle Cleaning: Use a soft, damp cloth with mild detergent to clean your porcelain. Avoid abrasive sponges that can scratch the surface.
- Avoid Sudden Temperature Changes: Don’t subject porcelain to sudden temperature shifts; it could lead to cracking. That means no hot tea in a cold cup straight from the cabinet.
- Proper Storage: Store porcelain with care. If you must stack, cushion between pieces with soft material.
Step-by-Step Porcelain Repair Guide
For Small Chips and Cracks
- Clean the Area: Start with a clean surface. Use a mild cleaner and let the piece dry completely.
- Apply Epoxy: Mix a two-part clear epoxy according to instructions. Apply it carefully to the chip or crack with a toothpick for precision.
- Clamp if Necessary: If the break is clean, you may need to hold the pieces together with a clamp until the epoxy sets.
- Remove Excess: Wipe away any excess epoxy with a damp cloth before it hardens.
- Cure: Allow the epoxy to cure as directed, typically 24 hours.
- Sand and Paint: Once cured, lightly sand if necessary and use porcelain paint for touch-ups to match the original color.
For Larger Breaks
- Gather All Pieces: If the item is broken into larger pieces, make sure you have all the parts.
- Clean and Dry: Clean each piece with mild soap and water. Dry thoroughly.
- Apply Adhesive: Apply a thin layer of epoxy to one edge of the break. Press the matching piece to it gently.
- Secure in Place: Use painter’s tape or a soft clamp to hold the pieces together while the epoxy cures.
- Cure and Clean Up: Allow the adhesive to cure fully. Clean up any excess with a razor blade if needed.
- Finishing Touches: Use porcelain paint to cover any repair lines and restore the piece’s original appearance.
Remember, repaired porcelain should be treated as decorative after repair; it might not be suitable for food use or washing due to the materials used in the repair process. Always handle with care, and your porcelain can be enjoyed for many years to come.
Collecting Porcelain: A Guide for Enthusiasts
Collecting porcelain is more than a hobby; it’s a journey through history and artistry. Whether you’re drawn to the delicate work of European masters or the subtle elegance of Asian ceramics, here’s how to start your collection on the right foot.
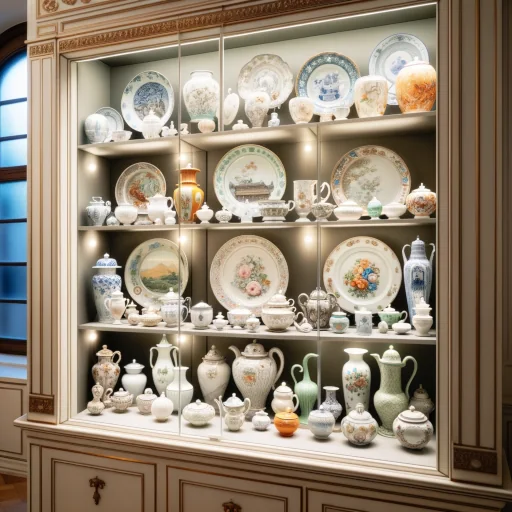

Starting Your Collection
- Research: Immerse yourself in the world of porcelain. Learn about the different styles, periods, and what distinguishes one maker from another.
- Define Your Interest: Decide whether you’re captivated by a particular era, style, region, or maker. This will focus your collection and make it more meaningful.
- Set a Budget: Porcelain can range from affordable to investment-level prices. Determine your budget and stick to it.
Where to Buy
- Auctions: Reputable auction houses are treasure troves for porcelain. They offer a variety and authenticity but remember to factor in buyer’s premiums.
- Antique Shops and Shows: These can be great for finding pieces, and you’ll have the chance to inspect the porcelain in person.
- Online Marketplaces: While convenient, be cautious. Ensure there’s a good return policy and that sellers have credible reviews.
What to Look For
- Condition: Check for chips, cracks, crazing, or restoration work. The better the condition, the more valuable the piece.
- Marks and Signatures: Familiarize yourself with maker’s marks and artist signatures which can often be found on the bottom of the piece.
- Provenance: A well-documented history of the piece can add to its value and authenticity.
Authenticating Antique Porcelain
- Expert Evaluation: If possible, have an expert look at the piece. They can provide insights into its authenticity and value.
- Maker’s Marks: Research marks and compare them with verified marks in porcelain databases or reference books.
- Quality of Workmanship: High-quality painting, glazing, and finishing are good indicators of authentic pieces.
- Wear and Patina: Genuine antique porcelain will show some signs of wear; too pristine could mean a reproduction.
Collecting porcelain is a rewarding experience that offers a tangible connection to the past and the beauty of fine craftsmanship. With patience and knowledge, you’ll build a collection that reflects both personal taste and the rich history of porcelain art.
Conclusion and Summary

The allure of porcelain lies in its paradoxical nature, as durable as it is delicate, as timeless as it is ever-evolving. From its ancient origins to its modern-day incarnations, porcelain continues to capture our imagination. It’s not just a material but a canvas that has recorded human history, carried cultural exchanges, and showcased artistic evolution.
In today’s world, porcelain is not bound by tradition; it is enhanced by it. The advances in technology and a growing consciousness about sustainability have opened new horizons for this noble material. 3D printing and energy-efficient kilns are but a glimpse into its potential.
Yet, the heart of porcelain remains in its beauty, whether it graces a collector’s cabinet or becomes an integral part of our homes and cities. As we continue to innovate and push the boundaries of what porcelain can be, it stands as a testament to human creativity — a blend of art, science, and the magic of transformation. Porcelain, in its elegant resilience, continues to be a cultural touchstone and a beloved jewel in the crown of ceramics.
Resources for Further Exploration
For those enchanted by the world of porcelain, there is a wealth of resources waiting to be explored. Here is a curated list of museums, exhibitions, and literature that will deepen your appreciation and understanding of this exquisite material.
Museums
- The Victoria and Albert Museum, London: Home to an extensive collection of ceramics, including a stunning array of porcelain from around the world.8
- The National Palace Museum, Taipei: Houses one of the largest collections of ancient Chinese imperial porcelain.9
- The Dresden Porcelain Collection, Germany: Features porcelain masterpieces, highlighting the craftsmanship of historic Meissen porcelain.10
- Musée National de Céramique, Sèvres, France: Offers a comprehensive look at French porcelain, with pieces dating back to the 18th century.11
Exhibitions
- “Flight of Fancy: The Galle Chateau Porcelain Room”: An immersive exhibit showcasing European porcelain artistry.12
- “Porcelain Power: Dynamic Porcelain Art from Ancient to Modern”: A traveling exhibition that illustrates the evolution of porcelain across different cultures.
Books
- “Porcelain: A History from the Heart of Europe” by Suzanne L. Marchand: Explores the fascinating history of European porcelain.13
- “The White Road: Journey into an Obsession” by Edmund de Waal: Part memoir, part history, this book delves into the obsession with porcelain across ages and continents.14
Whether you prefer to wander through galleries of gleaming porcelain or cozy up with a good book that transports you to the kilns of ancient dynasties, these resources offer a pathway to further discovery. Each one promises to enrich your journey through the enchanting world of porcelain.
Interactive Porcelain Q&A Section
Kaolinite clay is the primary ingredient in porcelain, giving it its distinctive translucency and strength when fired at high temperatures.
Antique porcelain can often be identified by its maker’s mark, signs of age such as crazing or patina, and the quality of craftsmanship.
No, porcelain is also used in technology, architecture, and art due to its durability, beauty, and insulating properties.
Frequently Asked Questions About Porcelain
Q1: What is the main component that gives porcelain its strength and translucency?
- A1: The main component is kaolinite clay, which, when fired at high temperatures, provides porcelain its unique properties.
Q2: How can I identify antique porcelain?
- A2: Look for maker's marks, quality of craftsmanship, signs of aging like crazing or patina, and documentation of the item's history.
Q3: Besides dishes and figurines, what are some modern uses of porcelain?
- A3: Porcelain is widely used in dental prosthetics, electrical insulators, architectural elements, and various art forms due to its versatility.
Q4: Is it safe to put antique porcelain in the dishwasher?
- A4: Generally, it is not recommended to put antique porcelain in the dishwasher as it can damage the glaze and artwork.
Q5: Can repaired porcelain still be used for dining?
- A5: Repaired porcelain is best used for decorative purposes, as the materials used for repair may not be food-safe.
Q6: Where is the best place to start looking for pieces to add to my porcelain collection?
- A6: Start at reputable auction houses, antique shops, and shows. Online marketplaces can be useful, but always verify the seller's credibility and return policies.
Footnotes
- https://www.archdaily.com/948466/the-benefits-of-ceramic-facade-cladding-in-3-remarkable-architectural-projects ↩︎
- https://www.florim.com/en/blog/furnishing-with-large-format-tiles-suggestions-from-the-world-of-interior-design/ ↩︎
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Arita_ware ↩︎
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Meissen_porcelain ↩︎
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Limoges ↩︎
- https://design.ncsu.edu/blog/2022/06/14/3d-printed-ceramics/ ↩︎
- https://www.keithcompany.com/traditional-ceramics-kilns.html#1 ↩︎
- https://www.vam.ac.uk/ ↩︎
- https://www.npm.gov.tw/?l=2 ↩︎
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dresden_Porcelain_Collection ↩︎
- https://www.sevresciteceramique.fr/en.html ↩︎
- https://www.getty.edu/art/exhibitions/chandelier/ ↩︎
- Marchand, Suzanne L.. Porcelain: A History from the Heart of Europe. United Kingdom: Princeton University Press, 2022. ↩︎
- de Waal, Edmund. The White Road: Journey Into an Obsession. United Kingdom: Farrar, Straus and Giroux, 2015. ↩︎





